Characteristics of the PUGNP wire and the causes of its danger
Labeling Explanation
The name of the PUGNP wire is deciphered as follows:
- P - wire.
- UN - universal.
- G - flexible.
- P is flat.
You may have noticed that the letter G is not in its place in the designation, because the letters UN - mean "universal. It is not known why this happened. But it should be said that there is a monolithic PUNP wire. By the way, it happens in both copper and aluminum versions, otherwise its technical characteristics are similar to PUGNP.
The cross-sectional area of the core is also indicated in the marking, type:PUGNP 2x2.5.This designation stands for 2 wires of 2.5 mm2. The actual cross section may be lower than 30% of the nominal. This is due to the fact that the technical specification for which this wire is manufactured does not regulate strict compliance with the cross section, in it the permissible error in the manufacture is 30%. This means that the claimed 1.5 "squares" can in reality be equal to 1, which in practice is a great danger.
Design
The wire consists of two or three flexible multi-wire cores, each of which is enclosed in insulation, all cores are covered with a layer of general insulation. In PUGNP, the neutral conductor is marked in blue, and in the three-core version, it is green-yellow (stripes) ground. The outer insulation is white, as can be seen in the photo below. This ends the description of the external parameters. It is produced according to the technical specifications of TU 3551-001-97568813-2008.
main parameters
Technical characteristics of the PUGNP wire:
- The cores are made of copper, at least 7 wires with a thickness of 0.3 mm each.
- Voltage: 450V DC, 1000V AC.
- Insulation material - PVC.
- Operating temperature range from -50 ° C to + 50 ° C. With prolonged heating can withstand up to 70 ° C, and with short-term + 80 ° C.
- The installation temperature is not lower than -15 ° C, with greater frost, the insulating layer may be damaged.
- Mounting Type - Fixed.
- Flexibility: at least 10 outer diameters of the wire.
- Environmental humidity up to 100% (at t = + 35 ° C).
- The term of operation is 15 years.
- Insulation resistance 10 MΩ.
- Construction length from 100 m.
- Core section range for two core wires from 0.35 mm2 up to 6.0 mm2, for three-core - from 0.35 mm2 up to 4.0 mm2.
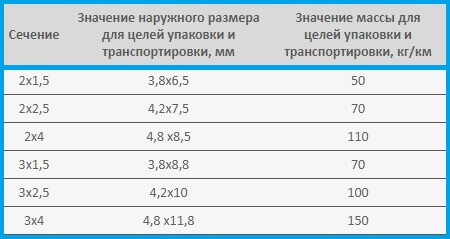
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the table of weight and outer diameter for certain sections of the PUGNP wire:
There are many manufacturers on the market that produce PUGNP. It is worth noting that the technical specifications depend on the responsibility of the manufacturer. Among them are:
- JSC Belaruskabel, Mozyr
- Luke-Cable LLC, Great Luke
- LLC TD PromEl, Oryol
Application area
The wire is designed to connect lighting circuits up to 250V ~. However, the technical characteristics make it possible to use it to power power circuits, such as sockets. The permissible cable current depends on its cross-section, therefore, it should be noted that the maximum cross-section of PUGNP conductors is up to 6 mm2. This must be taken into account when calculating the current load.
As already mentioned, this conductor is prohibited by the PUE. There are several reasons for this:
- It is produced according to outdated technical specifications with large cross-section tolerances. In addition, the nominal cross-section in one place of the wire does not guarantee that it will be unchanged along its entire length. It is possible that in some places the vein will be thinner.
- Thin insulation. The insulation layer of PUGNP on the core reaches 0.3 mm in the worst case, the outer layer - up to 0.5 mm. Moreover, according to the PUE, the minimum insulation thickness should be from 0.4 mm. This leads to slight damage to the insulating layer. When laying it is worth considering. Open laying, laying in the ground or in water is undesirable (most likely unacceptable). You need to use the corrugation cable channels or metal pipes.
- Thin insulation leads to increased danger. fire wiring.
However, despite the prohibitions, often this conductor is used for time lines. For overhaul of wiring, we strongly recommend that you look at other cables. What can replace PUGNP? For high-quality wiring, you can use a cable VVG, VVGng or NYM - These are its analogues, which are not prohibited by the PUE.
Similar articles: