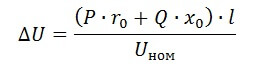Online calculation of cable voltage losses
Voltage losses in the cable are a big problem in the case of a long path from the power source to the consumer, as well as the high power consumption of the latter. Incorrect materials for the electric line (wiring), for example, wires with very thin cores, begin to heat up due to the low conductivity for the electric current. The calculator provided by us allows you to calculate the voltage loss in the cable online:
Also, let's see where the losses come from and why. Conductors are made of copper and aluminum, although they are excellent conductors, but still have a certain resistivity, which is active. On any resistive element, a certain amount of volts drops, according to Ohm's law:
U = I * Rprov
In direct current calculations, only active resistance R appears in the cable losses calculations. At the same time, when working with alternating current, for example, in 0.4 kV networks, the reactive part is added to the active value - they make up the total resistance Z (Xl and Xc) . The role of reactive power is very important in the calculations, since it is 20 percent or more of the power consumption.
Why is such a calculation necessary? Everything is very simple: the more R wiring - the more losses, and the stronger the wires are heated. Let's figure out how to calculate them manually, but it's easier to do this using an online calculator. The formula for determining the resistance of a conductor is as follows:
R = p * L / S
Where:
- p is the resistivity;
- L is the length;
- S is the cross-sectional area.
It follows that it depends on the length and cross-sectional area. The longer and thinner the conductor - the greater R, and to reduce it, conductors with a large cross section are needed.
Then, in the simplest case, the losses are equal to the voltage drop on the line:
dU = I * Rprov
And given the full power for AC:
But the first formula is valid only for one of the conductive conductors, and electricity, as you know, cannot be transmitted through a single wire. It is transmitted at least in two, in a three-phase network - in four wires.
To simplify your calculation and save valuable time, use the online calculator to calculate the voltage loss in the cable. To do this, you must enter the parameters:
- length
- cross-sectional area of conductive conductors;
- amount of current consumption or power;
- number of phases;
- conductor temperature;
- COS F.
As a result, in a couple of clicks the online calculator will provide you with the following data:
- losses;
- cable resistance;
- reactive power;
- load voltage.
Related materials: