What is earthed neutral - simple definition
Dummy-grounded neutral is part of the power supply system of consumers, it is aimed at the safe use of networks up to 1000 Volts, which are most often used in everyday life and in production as a source of a standard level of low voltage - 0.38kV, 0.22kV and below. Neutral is a common point of connection of star windings at power sources, which are transformers or generators. If this point is connected to the earth, then we get a network with a grounded neutral. At the zero point, potential equalization occurs, which is very convenient for providing electric power to both single-phase and three-phase sources.
The device and principle of operation of networks with earthed neutral
The principle of operation of electric power sources, in particular, step-down transformers, is based on the law of mutual induction and transfer of energy through a magnetic core. In this case, the primary winding may not have a neutral wire, unlike the secondary one, where connecting it to zero through a low-resistance conductor, which can be equated with a zero value, will be an effective means of protecting people from voltage damage that is dangerous to their life and health.
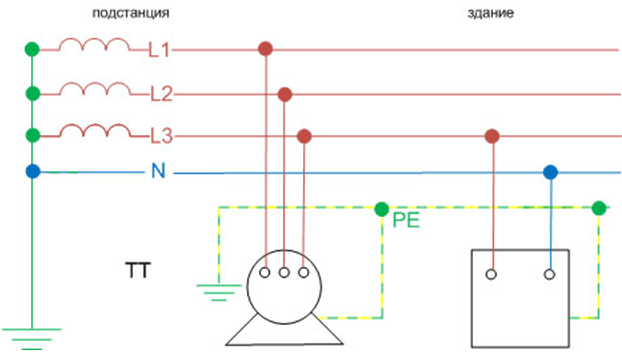
The main feature of networks with earthed neutral is the appearance of not only linear, but also phase voltage. What is it and how does it differ from each other, let us consider an example of a simple circuit diagram.
Phase voltage is the potential between one of the wires of the line and the zero point connected to the ground, that is, tightly grounded. Line voltage is the potential difference between the two outputs of the lines, that is, L1 and L2, L1-L3, or L2-L3, it is also called interphase. Such sources of electrical energy in everyday conditions have a common voltage value in the form of 380 V - linear, and 220 - phase. Linear voltage is greater than phase voltage by √3, i.e. by 1.72.
But the main task of such a system is not only the transportation of voltages of two values to consumers with a different number of phases in one power supply system, but also the protection of a person during breakdown of insulation and the appearance of voltage at points that in the normal state do not have a dangerous potential. In residential buildings it is:
- cases of all household appliances that conduct electric current, that is, are made of steel or other conductive metal;
- metal structures of switchboards and switchgears;
- cable sheath.
Also, to ensure safety, all of the above items must be grounded, in this case the danger from the use of voltage and the use of household appliances in networks with a grounded neutral will be minimal. Moreover, uniformity of distribution of single-phase loads is mandatory for such circuits.
Explanation for dummies
The step-down substation in which the transformer is installed has its own ground loop. It is interconnected by steel tires and rods, in one ground loop. A cable is laid to consumers in the electrical panel from the substation, which contains four cores. If the consumer needs power from a three-phase circuit of 380 volts, then you need to connect to all cores. In a single-phase 220 V network, power will be supplied from the neutral wire and from one of the phases. Protection of people in single-phase and three-phase circuits, if there is no grounding system, should be carried out due to special protective shutdown devices (RCD), which are triggered by a small leak to zero, while disconnecting the consumer reliably from the network.
Classification of networks with earthed neutral
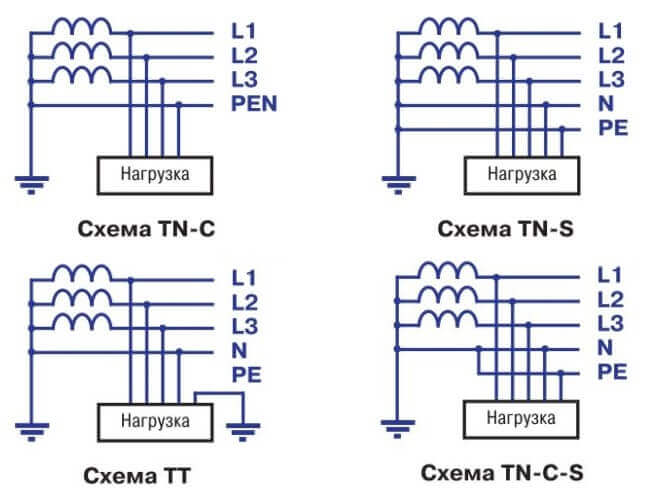
The modern power supply system has a standard marking where, in addition to the working neutral conductor, there is also a protective conductor, which gives a definition of the degree of protection.
- L is the phase conductor;
- N is the working zero;
- RE - protective neutral conductor;
- PEN - working and neutral conductor made by one wire.
There are several subsystems in circuits with an energy source that has a grounded neutral:
- TN-C. With this system, the neutral and protective conductor from the substation is organized by one conductor, near the receiver its case (or other elements to be earthed) are connected to this combined conductor - this is called grounding. This is an outdated system that was used in old houses under the USSR; now it is not used for household consumers, as it is unsafe. Such a system has a significant drawback, since in the event of a PEN conductor breakdown on the way from the supply transformer to the power receiver, a dangerous potential appears on the nullified equipment cases. It is used only to protect industrial consumers (this is described later in the next section).
- TN-S. Has a higher percentage of safety during emergencies. This is achieved by separating the protective and working conductors along the entire length of the supply line, from the transformer to the distribution switchboard (to the end consumer). However, due to the fact that it is necessary to use cable products with five cores, which greatly increases the cost of laying and the budget for the organization of power supply to the consumer, this system is not always used.
- TN-C-S. This grounding system is the most common in our time. With this system, the neutral and protective conductors along the entire length of the line are combined into one combined PEN conductor. Upon entering the building, this conductor is divided into protective PE and zero N, which are further distributed to consumers (apartments). With this system, if the PEN conductor is burned to the separation point, hazardous potential will appear on the grounded housings of electrical appliances. To prevent this, repeated grounding of the PEN conductor is made along the entire length of the line and at the entrance to the building and increased requirements are placed on the mechanical protection of this conductor.
- TT. This grounding system is practiced if the line of the TN-C-S system is in an unsatisfactory technical condition and the safety of the protective grounding provided for in it is not ensured. This grounding system provides for the installation of an individual grounding loop at the consumer, while the PEN conductor of the electrical network is used only as the neutral wire N.
It's important to know
For power supply of single-phase and three-phase consumers in industry and in domestic conditions, the so-called grounding, which is supposedly an effective method for automatically shutting down an electrical installation or a part of it in which a short circuit has occurred.When grounding in circuits with a grounded neutral, all metal parts and cases of electrical equipment are connected to the zero wire. How does this protection work? The fact is that with any short circuit to the case, the circuit goes into short circuit mode, the current in the circuit breaker circuit increases greatly and the emergency section is disconnected from the network.
The advantage of such a system is the saving of expenses for protective grounding wiring, as well as reducing the cost of cable products, since both single-phase and three-phase power receivers can be connected to the same circuit.
However, the lack of a grounded neutral, organized by the principle of protective grounding, can be called the lack of human protection in the event of breakdown of insulation on the appliance body during a zero wire break, which is also protective. And this is a very important point - grounding is a dangerous measure of protection, therefore it should not be organized at home!
Modern power supply is nevertheless aimed more at safety, therefore it requires the installation of an RCD and a separate protective grounding circuit, through which even the smallest leakage currents will go to the ground, without endangering the person.
Now you know what a neutral earthed neutral is, what is its operating principle and in what networks it is used. If you have any questions, you can ask them in the comments under the article!
Related materials: