What is the anode and cathode - a simple explanation
Electrochemistry and Electroplating
There are two main sections in electrochemistry:
- Galvanic cells - the production of electricity through a chemical reaction. These elements include batteries and accumulators. They are often called chemical current sources.
- Electrolysis - the impact on a chemical reaction with electricity, in simple words - with the help of a power source, a reaction starts.
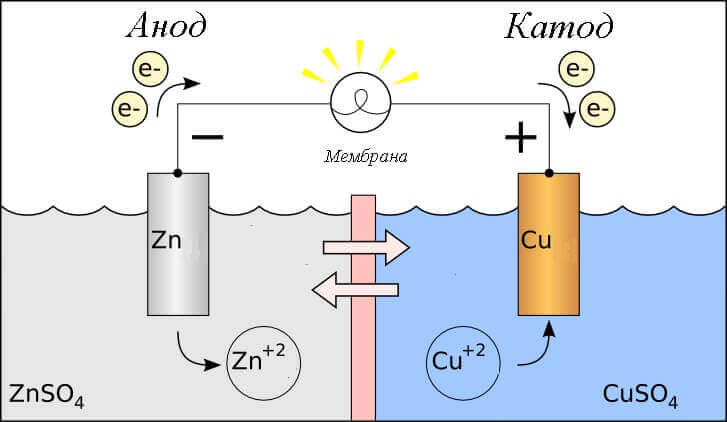
Consider the redox reaction in a galvanic cell, then what processes occur on its electrodes?
- Anode - the electrode on which is observed oxidative reactionthat is, hegives electrons. The electrode on which the oxidation reaction occurs is called reducing agent.
- Cathode - the electrode on which flows recovery reactionthat is, heaccepts electrons. The electrode on which the reduction reaction occurs is called oxidizing agent.
This begs the question - where is the plus, and where is the minus of the battery? Based on the definition of a galvanic cell anode gives electrons.
Important! GOST 15596-82 gives an official definition of the names of the conclusions of chemical current sources, in short, then plus on the cathode, and minus on the anode.
In this case, the flow of electric current is considered. along the conductor of the external circuit from oxidizer (cathode) to reductant (anode). Since the electrons in the circuit flow from minus to plus, and electric current is vice versa, then the cathode is a plus, and the anode is a minus.
Attention: current always flows into the anode!
Or the same in the diagram:
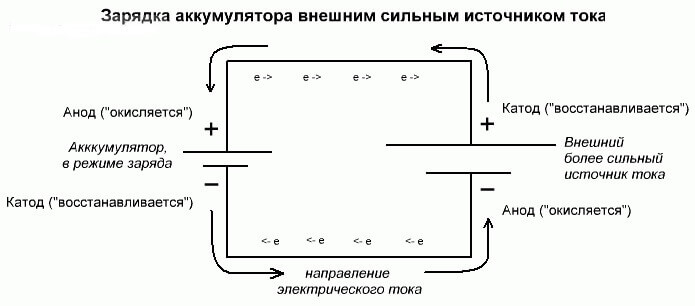
Battery electrolysis or charging process
These processes are similar and inverse to the galvanic cell, since here not energy comes from a chemical reaction, but rather a chemical reaction occurs from an external source of electricity.
In this case, plus the power source is also called the cathode, and minus the anode. But the contacts of the rechargeable galvanic cell or electrodes of the electrolyzer will already have opposite names, let's see why!
Important! When a galvanic cell is discharged, the anode is minus, the cathode is plus, and vice versa when charging.
Since the current from the positive terminal of the power source is supplied to the positive terminal of the battery, the latter can no longer be a cathode.Referring to the foregoing, we can conclude that in this case the electrodes of the battery conditionally change places when charging.
Then, through the electrode of a charged galvanic cell into which an electric current flows, it is called an anode. It turns out that when charging the battery, the plus becomes the anode, and the minus the cathode.
Electroplating
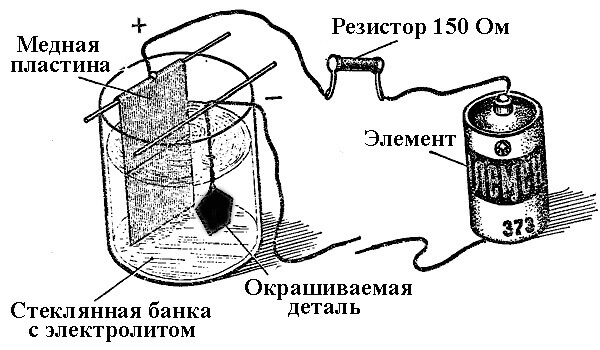
The processes of metal deposition as a result of a chemical reaction under the influence of an electric current (during electrolysis) are called galvanic engineering. Thus, the world received silver-plated, gilded, chrome-plated or other metal-plated jewelry and details. This process is used both for decorative and for applied purposes - to improve the corrosion resistance of various components and assemblies of mechanisms.
The principle of operation of electroplating plants lies in the use of salt solutions of the elements that will cover the part as an electrolyte.
In electroplating, the anode is also an electrode to which the positive output of the power source is connected, respectively, the cathode in this case is a minus. In this case, the metal is deposited (reduced) on the negative electrode (reduction reaction). That is, if you want to make a gilded ring with your own hands - connect the negative output of the power supply to it and place it in a container with the appropriate solution.
In electronics
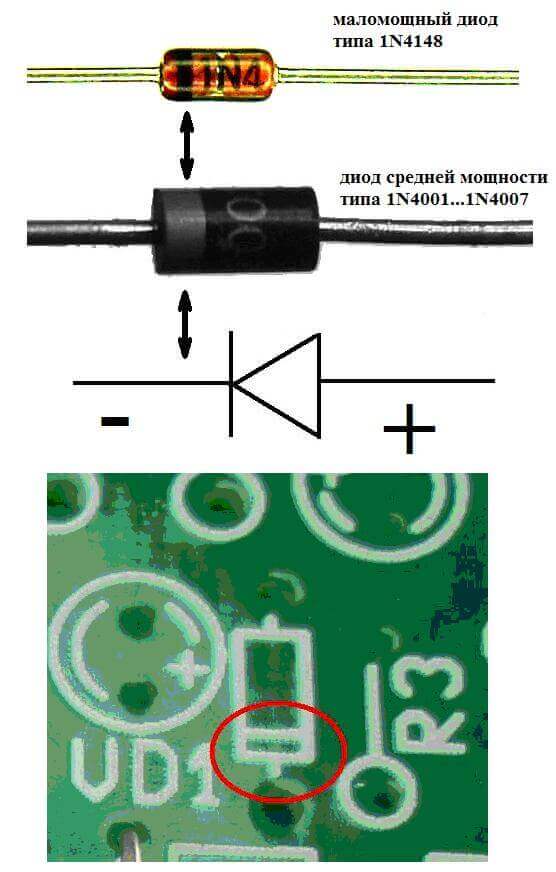
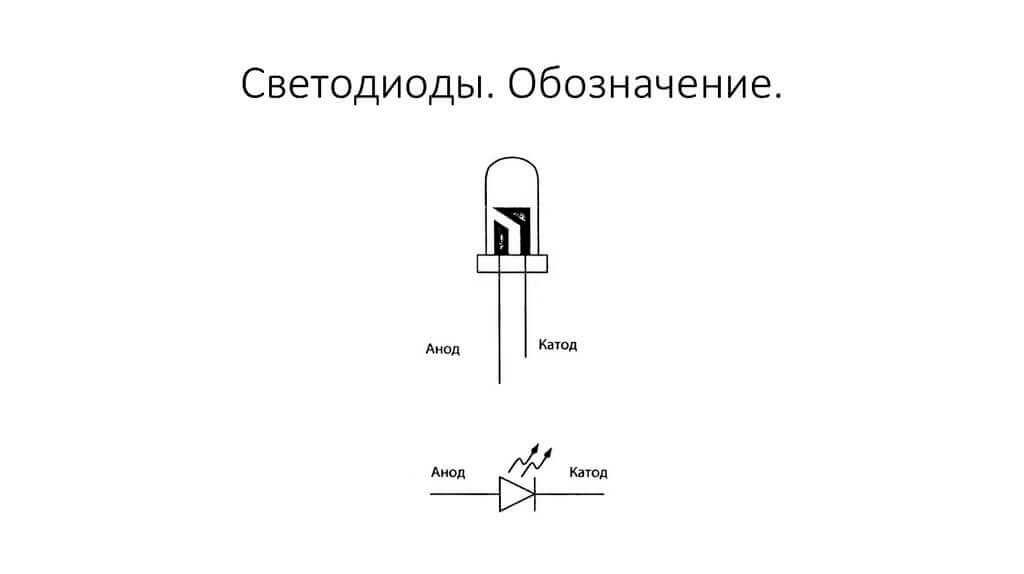
The electrodes or legs of semiconductor and vacuum electronic devices are also often called the anode and cathode. Consider the conditional graphic designation of a semiconductor diode in the diagram:
As we see, the anode of the diode is connected to the plus of the battery. It is so called for the same reason - in this case, the current flows into the diode's output in any case. On a real element on the cathode there is a marking in the form of a strip or a dot.
The LED is similar. On 5 mm LEDs, the insides are visible through the flask. The half that is larger is the cathode.
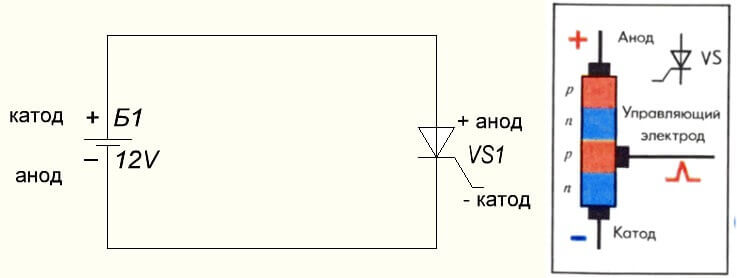
The situation is also with the thyristor, the purpose of the conclusions and the “unipolar” application of these three-legged components make it a controlled diode:
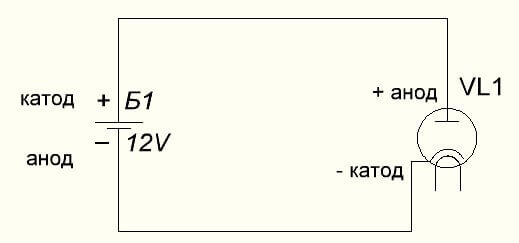
The vacuum diode also connects the anode to the plus, and the cathode to the minus, which is shown in the diagram below. Although when applying reverse voltage, the names of these elements will not change, despite the flow of electric current in the opposite direction, albeit insignificant.
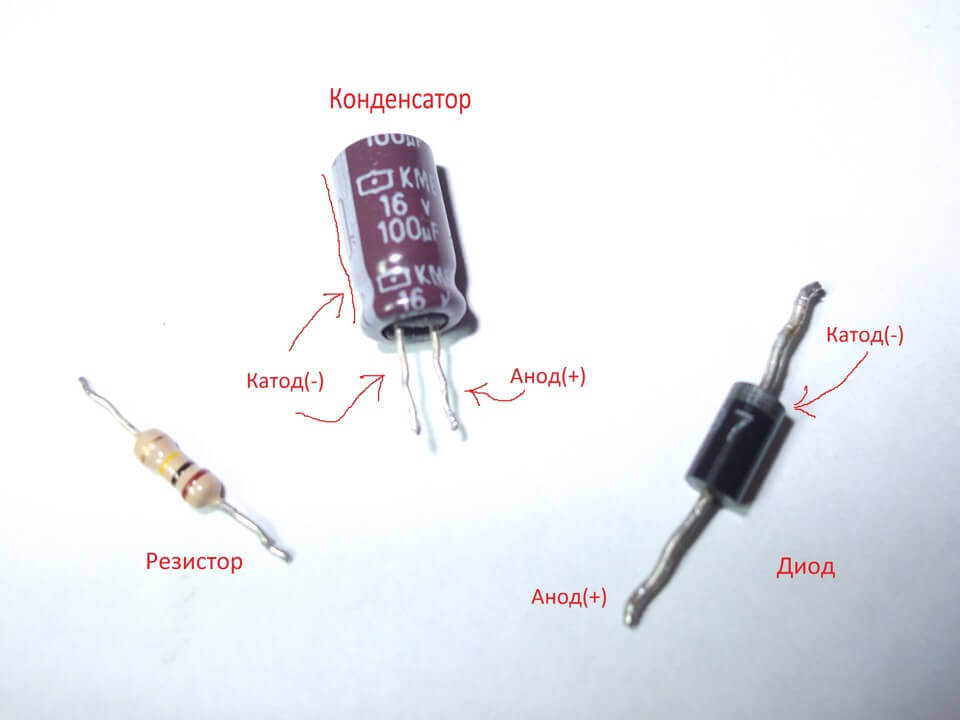
With passive elements such as capacitors and resistors, this is not the case. The cathode and anode are not isolated separately from the resistor; current in it can flow in any direction. You can give any name to its conclusions, depending on the situation and the scheme in question. Conventional non-polar capacitors also. Less commonly, this separation of contact names is observed in electrolytic capacitors.
Conclusion
So, to summarize, answering the question: how to remember where is the plus, where is the minus of the cathode with the anode? There is a convenient mnemonic rule for electrolysis, battery charge, electroplating and semiconductor devices. These words with similar names have the same number of letters, as illustrated below:
In all these cases, the current flows from the cathode, and flows into the anode.
Do not be confused by the confusion: “why is the cathode positive for the battery, and when it is charged, does it become negative?” Remember for all elements of electronics, as well as electrolyzers and in electroplating - in general, for all energy consumers, the anode is the output connected to the plus. The differences end there, now it’s easier for you to figure out what is the plus and minus between the outputs of the elements and devices.
Finally, we recommend watching a useful video on the topic of the article:
Now you know what the anode and cathode are, as well as how to remember them quickly enough. We hope the information provided was useful and interesting for you!
Related materials: